- HTTP
- SSL
- LDAP
- JDBC
- Servlet/JSP
- SQL
- HTML
- XML
Friday, February 23, 2018
DevOps - Open Source - Document Databases - MongoDB, Kafka, Cassandra, Couchbase
MongoDB, Kafka, Hadoop, NonSQL, MySQL and other Open source systems.
Monitoring/reporting technologies for DevOps
Nagios, Graphite, Cacti, AppDynamics, NewRelic, Splunk, Graylog etc
Big brother Monitoring :
Unix/Linux Machine - Operations :
---------------------------------
1) App Servers
d) UtilityServers
e) Proxy Servers
4) Reporting
a) Tape Backups
b) VM Host Servers
conn
trends
Big brother Monitoring :
Unix/Linux Machine - Operations :
---------------------------------
1) App Servers
- Info - Provides OS and Hardware information, such as versions and number of cpus. Provided by script bb-sysinfo.sh. Informational only, should never be anything but Green.
- Stats Provides system runtime information, such as
- uptime,
- vmstat,
- iostat and swap space.
- informational only, should never be anything but .
- apps
- conn
- cpu
- dbprocs
- disk
- fd
- inode
- memory
- msgs
- nfs
- procs
- reboot
- ssh
- trends
2) File Servers
a) Monitoring
b) FTP Servers
c) Nameserversd) UtilityServers
e) Proxy Servers
4) Reporting
a) Tape Backups
b) VM Host Servers
conn
trends
Linux administration experience for DevOps
(e.g. Ubuntu, RedHat/CentOS) with a focus on web (Apache/Nginx)
Types of errors in Linux/Unix administration
- 100 - Disk Error. Disk is over 95% full...
- 200 - CPU Error. CPU load average is unacceptably high.
- 300 - Process Error. An important processes has died.
- 400 - Message file contains a serious error.
- 500 - Network error, can't connect to that IP address.
- 600 - Web server HTTP error - server is down.
- 610 - SSl Cert check failure, Cert will expire in 7 days or less.
- 7-- - Generic server error - 7 + server port number i.e. 721 = ftp down
- 800 - DNS server on that machine is down
- 911 - User Page. Message is phone number to call back.
- 999 - The service reported in an error could not be found in the svcerrlist token in etc/bbwarnsetup.cfg file.
Thursday, February 22, 2018
Maven - a2z
Maven
Maven is a Build tool
Maven provides
-> Compile the source code.
-> Generate jar, war, ear.
-> Deployment
-> Generate the reports like code quality, code coverage.
-> Generate the documentation.
Maven’s project goal
Maven's primary goal is to allow a developer to understand the complete state of a project in the shortest period of time.
Maven’s Objectives
- It makes the build process easy.
- Provides a uniform building system.
- Provides quality related project information .
- Provides guidelines related to development to meet the best goal.
- Allows transparent migration to new features.
Maven’s Features
- Superior dependency management.
- A large repository of libraries and metadata.
- Multiple projects handling.
- Extensible, easy to write plug-in.
- Coherent site of project information.
- Multiple language support – C++, Java …
- Maintainability: stop building the build. Focus on the application.
2) Maven Software Installation :
-> It is an opensource software
-> It is in the form of zip file
-> Download maven.zip freely from http://apache.osuosl.org/maven/maven-3/3.5.4/binaries/apache-maven-3.5.4-bin.zip
After extracting the maven zip file, the maven root folder will be having
bin -> mvn.bat
conf -- settings.xml
lib -- jar
plugins - predefined.
-> Latest version : 3.5.x
from 3.3 -- JDK 1.7 or above is using
< maven 3.3 -- jdk 1.6 is using.
Note : Q) How to enable maven software ?
Maven is completely written in java, so it must compatible with the respective Java version
In windows operating systems - > Properties -> settings ->environment variables set below
JAVA_HOME = C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_131
Path = C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_131\bin or %JAVA_HOME%/bin
Maven project structure
2) Importance of pom.xml
A Project Object Model or POM is the fundamental unit of work in Maven. It is an XML file that contains information about the project and configuration details used by Maven to build the project.
--> Pom stands for project objective model.
-> It contains information about how to generate jar, war, ear and also how to generate the reports like codequality, code coverage..
-> Every pom.xml have 3 elements are mandatory.
1. Groupid - group name for jar, war, ear
2. Artifactid - jar or war or ear name
3. Version -- version of jar or war
Examples :
---------------
com.dev21(Groupid) : FirstApp(Artifactid) : 1.0-SNAPSHOT ( version)
Always the combination should be unique.
------------
<project>
<groupid>com.dev21</groupid>
<artifcatid>FirstApp</artifactid>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging> jar or war or ear or pom
</packaging>
</project>
Maven command operations
Types of Repositories :
1. Local Repository -- C:\Users\Sreenu\.m2
2. Remore Repository - client rep -- https://www.repo.hdfc.com/archive/project
3. Central Repository - https://repo.maven.org/artifacts/projects/..
Note : When we run the maven project first maven will look into local repo to find the dependencies.
If it is found then get from local rep.
--> If it is not found in local repo then it will go central repo, if it is found in central then get the dependencies from central repo.
--> If it is not found in central repo then it will go remote repo, if it is find in remote repo then get the dependencies from remote repo else it will give error no artifact found.
8) Importance of settings.xml
--> settings.xml file will configure locations of local repo and remote repo.
--> First maven software will read the pom.xml and start the search in local repo which is configured in settings.xml file.
--> The default local rep location : C:\Users\Sreenu\.m2 if you want we can update the new local repo location in settings.xml
--> maven software will refere new local repo instead of
9) Types of pom.xml
a) Normal pom.xml
b) Parent pom.xml
c) Super pom or Effective pom.xml
d) Aggregator pom or modules pom
Aggregator or modules pom.xml
Maven is the most popular Java Dependency Management Tool.
Thanks for referring this article, well, you may get much knowledge/learn all below areas by end of this article.
- Use Maven to Manage Dependencies
- Use Maven to create Multi Module Projects
- Understand Maven Best Practices
- Use Maven Commands
- Understand Maven Build Life Cycle and Project Object Model
- Understand Maven's philosophy of "Convention over Configuration"
- Use Maven to generate Projects using Maven Archetypes
- Use Maven Plugins
- Understand how to use Maven in combination with an IDE like Eclipse
We can automate all below listed ones using Maven :
- Compiling Java Code
- Running Unit Tests
- Building Jar's and Wars
- Running web applications in Tomcat
- Setting up new projects
Let's build some sample projects using below important Maven :
- Dependency Management - including Transitive Dependencies
- Maven Project Object Model
- Maven Build Life Cycle
- Maven Plugins
- Maven Archetypes - Generate Projects
- Maven Best Practices
- Multi Module Maven Projects
Target audience?
- You want to use Maven to manage Dependencies
- You want to use Maven to create New Projects
- You have familiarity with Java Programming
- You want to understand Maven Best Practices and a few Maven Tips and Tricks
- You want to understand how Maven Works
Requirements
- You should have familiarity with Java Programming.
- You should have access to internet to download and setup Maven and Eclipse
- We will help you setup Maven and Eclipse
- You should be ready to have fun doing a lot of hands-on stuff
Topics
1) Maven Basics
a : Magic of Maven - How does it help a developer?
b : Setting up Your First Maven Project
c : Your First Maven Dependency
d : Understand How to Build a Jar
e : Maven Goals - compile, test and install
f : Understand Maven Build Life Cycle
2) Maven Dependency Management
- Understand Maven POM - Project Object Model
- Transitive Dependencies
- Excluding Dependencies in Maven
- Scope of a Dependency
- Versioning of Dependencies
3) How does Maven Work?
4) Advanced Maven
- Maven Super POM and Effective POM - Convention over Configuration
- Understand How Maven Downloads dependencies - effective-settings
- Let's Play with Maven Plugins
- Maven from Command Line
- Basics of Multi Module Maven Project
- Best Practices of Multi Module Maven Project
- Running Web Application in Tomcat
- Maven Commands - Tips and Tricks
- Creating Projects with Maven Archetypes
5) Conclusion
Chef - Powerful automation platform to change Infra to code.
Chef
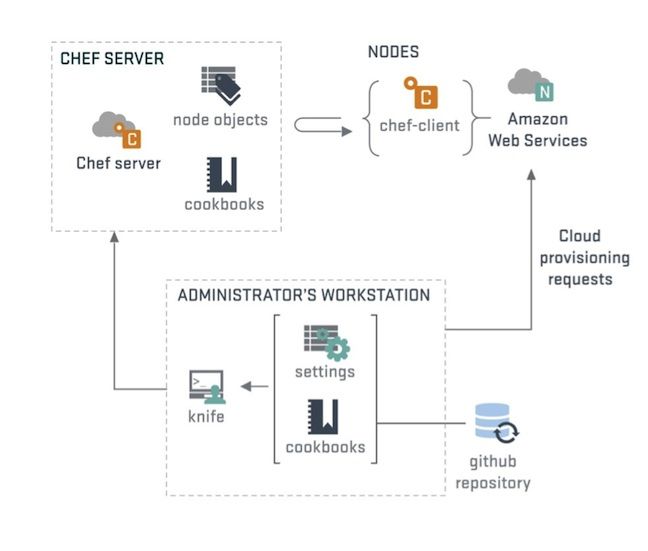
Chef is a powerful automation platform that transforms infrastructure into code. Whether you’re operating in the cloud, on-premises, or in a hybrid environment, Chef automates how infrastructure is configured, deployed, and managed across your network, no matter its size.
How Chef Works
Chef stores collections of recipes in a cookbook.
One cookbook should relate to a single task, but can have a number of different server configurations involved (for example a web application with a database, will have two recipes, one for each part, stored together in a cookbook).
There is a Chef server which stores each of these cookbooks and as a new chef client node checks in with the server, recipes are sent to tell the node how to configure itself.
The client will then check in every now and again to make sure that no changes have occurred, and nothing needs to change. If it does, then the client deals with it. Patches and updates can be rolled out over your entire infrastructure by changing the recipe. No need to interact with each machine individually.
References
Puppet - a2z
Introduction to Puppet Enterprise for your Linux Environment
Introduction to Puppet Enterprise for your windows Environment
If you're new to Puppet Enterprise, this is the webinar for you. You'll learn how Puppet helps lay the foundation for your DevOps practices, treats infrastructure as code, and achieves better collaboration between dev, ops, InfoSec, and networking. You'll see why thousands of companies rely on Puppet to automate the delivery and operation of their software and see it in action with a live demo.
In this recording we will show you the following in a Linux environment:
In this recording we will show you the following in a Linux environment:
- Installation of an agent
- Managing resources (packages, files, services, etc.)
- Granular visibility through reporting
- Managing change for more efficient workflows
We will also leave plenty of time after the presentation for questions.
Featured speakers: Abir Majumdar, Sales Engineer and Hannah Taylor, Sales Development Rep.
40 Minutes
US/Canada
Python for DevOps
https://github.com/EbookFoundation/free-programming-books/blob/master/free-programming-books.md#jenkins
Challenging Tasks for Automation/Automic Engineer - DevOps
- Automation/Automic Engineer include developing and managing build processes, using CA Automic's ONE Automation platform to support continuous integration, continuous delivery (application deployment) and supporting the applications and underlying tools to transform code into running products on a daily basis.
- Implement high availability code in UC4 - robust Automic's ONE Automation Engine (UC4) infrastructure
- How to do the below key activities :
- Installing and configuring Automation Engine
- Installing and configuring Utilities
- Installing and configuring Service Manager, Automic Deployment Nodes - Unix/Linux
- Installing and configuring FTP Agent
- Business Objects Agent
- Informatica Agent
- DB Agent
- Administrative task setup & configuration.
- Jobs :
- Experience in creating Jobs and define Job Properties for Informatica, BO, Web Services, FTP thru Automic Engine (UC4), calendars, schedules, dependency and orchestrate workflows.
- SCM Tasks :
- Contribute to the collection, development, review, and adoption of enterprise software build strategies, software branching strategies, configuration management, deployment practices and techniques.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Hyderabad Trip - Best Places to visit
Best Places to Visit in Hyderabad 1. 1. Golconda Fort Maps Link : https://www.google.com/maps/dir/Aparna+Serene+Park,+Masj...
-
· Common Core Math Activities http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/index.html · L...
-
1) Airport Address and links 2) Hotel address and links CoCo Key Hotel and Water Resort 7400 International Dr, Or...






